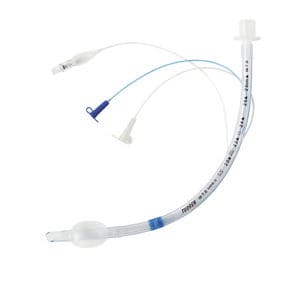
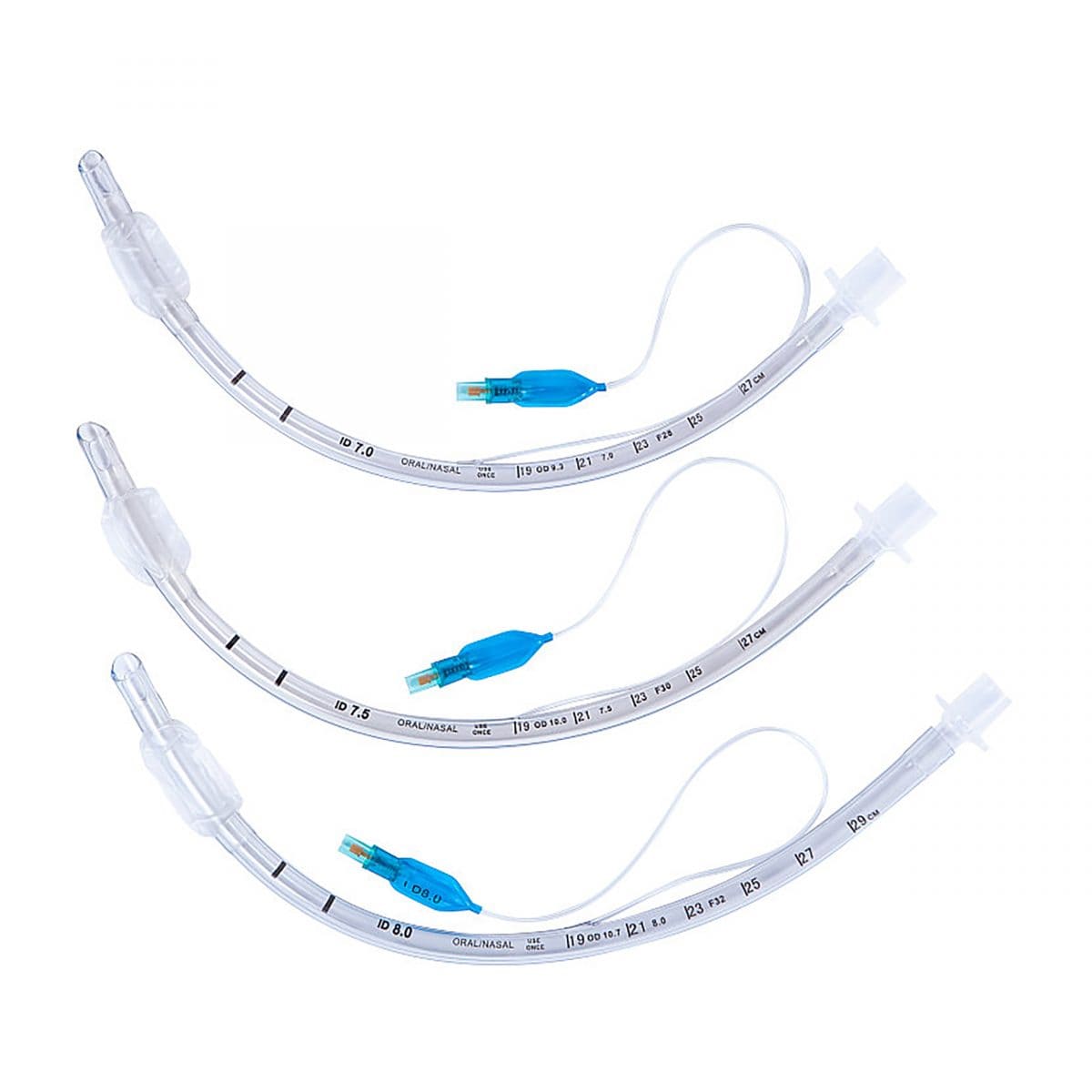
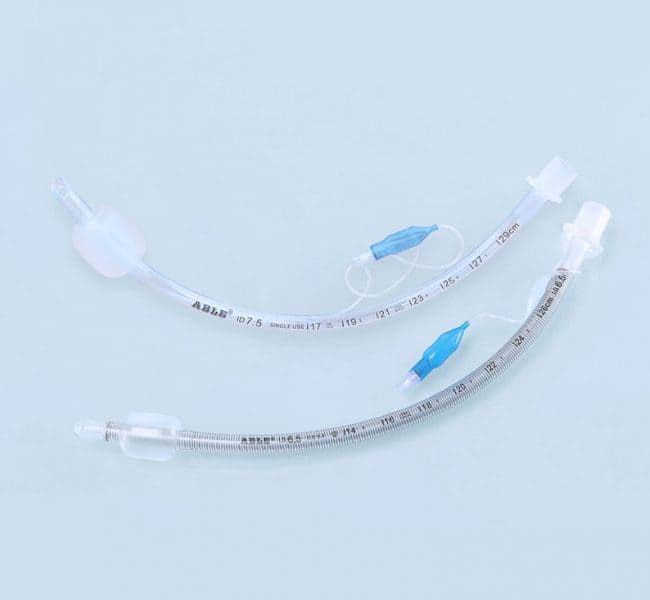
- Endotraecheal tubes (ETT) are medical devices used for the safe and efficient insertion of a breathing tube into the trachea of a patient.
- ETT is designed to provide maximum patient comfort and safety while providing effective treatment.
- It is an important tool in critical care operations, providing a controlled and secure airway for the patient while allowing the medical team to monitor and regulate their condition.
- ETT come in a variety of sizes, materials, and shapes, with each type having its own unique benefits and drawbacks.
- They have a long history of use in medical operations, with the most commonly used ETT being the cuffed endotracheal tube.
- Cuffed tubes are designed with a cuff which is inflated to seal the trachea and prevent air from entering from the sides of the tube.
- Other types of tube include uncuffed, high-volume low-pressure, and low-volume high-pressure ETTs.
- Depending on the patient’s condition, the medical team can choose the most suitable tube for their needs.
- Endotraecheal tubes are the most effective and efficient way to ensure safe and comfortable treatment for a patient suffering from respiratory distress, making them an essential tool in all critical care operations.